AFL++: fuzzing
Instrumentation
System setup
Fuzzing ROST
With a tuned dictionary
With grammar mutations
With mixed inputs
Minimal cases storage
AFL++: fuzzing
Fuzzing is one powerful way to identify bugs in software.
Running efficient fuzzing campaigns however require a suitable fuzzing environment. This page help to setup one for AFL++.
Instrumentation
The first step of fuzzing is to prepare the target with a special compiler which instruments the generated binary code.
Several compilers get available by installing the AFL++ package, for instance on Debian:
# apt-get install afl++
The source code can then get configured with the following commands:
./autogen.sh
CC=afl-gcc-fast ./configure \
--prefix=/dev/shm/fuzzing-sys
--enable-debug \
--disable-gtk-support \
--disable-curl-support \
--disable-python-bindings
Here are some explanations about the used arguments:
--prefix: install all the binaries in a temporary directory inside the RAM disk;--enable-debug: activate all theassert()checks inside the code;--disable-gtk-support: disable useless GUI code;--disable-curl-support: disable useless network code;--disable-python-bindings: disable heavy code linked to Python support.
As Chrysalide and ROST rely on plugins to extend their features, the --disable-shared switch advised by AFL++ is not suitable here and is then discarded.
Programs can be compiled and installed with:
make -j make install
System setup
A particular CPU schedule is required; it can be enabled by running the following command as root:
echo performance | tee /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu*/cpufreq/scaling_governor
In order to preserve disk lifespan, I/O get redirected to a RAM-disk thanks to the AFL_TMPDIR and other environment variables:
export AFL_TMPDIR=/dev/shm/afl-ramdisk export FUZ_IN=/dev/shm/afl-in export FUZ_OUT=/dev/shm/afl-out rm -rf "$AFL_TMPDIR" "$FUZ_IN" "$FUZ_OUT" mkdir -p "$AFL_TMPDIR" "$FUZ_IN" "$FUZ_OUT"
In order to turn any GLib warning into a crash, the following content has to be exported:
export G_DEBUG=fatal-warnings
Fuzzing ROST
The original rost binary can be fuzzed with the AFL @@ special argument pointing to a rule input file.
However, a special version suitable for the AFL persistent mode is also available. This extra version is able to scan files only, with rules provided by an AFL buffer.
A fast-rost program can thus be compiled and installed with:
make -C tools/fuzzing/rost/ install
With a tuned dictionary
AFL accepts dictionaries with the -x switch to help effortlessly exploring the valid grammar with known tokens.
Once the rost binary is compiled, a grammar file for ROST can be built by running a script available from the source package:
./tools/fuzzing/rost/gen-dict.sh cp tools/fuzzing/rost/rost.dict /dev/shm/
A basic rule definition is available to ignite the fuzzing process:
cp tools/fuzzing/rost/test.rost "$FUZ_IN"
The fuzzing process can then get launched:
afl-fuzz -i "$FUZ_IN" -o "$FUZ_OUT" -x /dev/shm/rost.dict -- /dev/shm/fuzzing-sys/bin/fast-rost /bin/ls
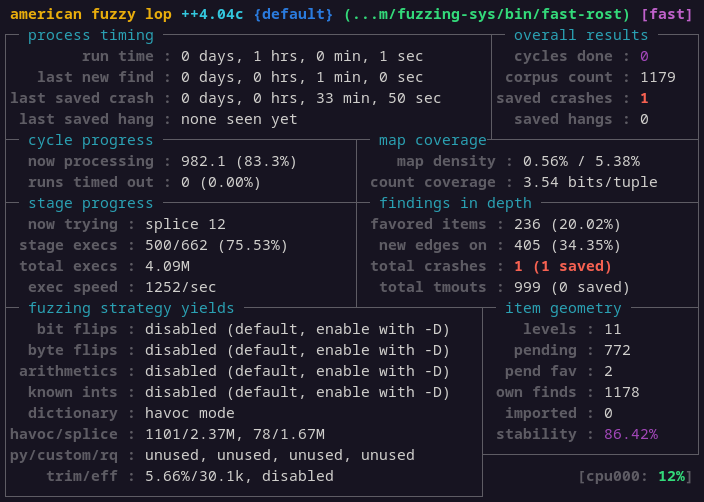
With grammar mutations
A grammar-based custom mutator for AFL++ can be used to handle all the details of the ROST grammar.
Such a tool can for instance be downloaded directly inside the Chrysalide's code source:
git clone https://github.com/AFLplusplus/Grammar-Mutator
Some mandatory packages have to get installed:
# apt-get install valgrind uuid-dev default-jre python3
The JAR file for the parser can be downloaded into any directory and its final location will be provided at compilation time:
wget https://www.antlr.org/download/antlr-4.8-complete.jar -O /tmp/antlr-4.8-complete.jar
The grammar definition has to be specified in JSON. A Python script is available to translate the ROST Bison grammar into this new JSON format:
python3 ./tools/fuzzing/rost/convert.py ./src/analysis/scan/grammar.y \
| tee Grammar-Mutator/grammars/rost.json
The grammar mutator for ROST can now get compiled:
make -j -C Grammar-Mutator \
ENABLE_TESTING=1 \
ANTLR_JAR_LOCATION=/tmp/antlr-4.8-complete.jar \
GRAMMAR_FILE=grammars/rost.json \
GRAMMAR_FILENAME=rost
Note : one can update the grammars/Grammar.g4 file without recompiling the whole project by running the following commands:
rm -rf Grammar-Mutator/lib/antlr4_shim/generated
make -C Grammar-Mutator \
ENABLE_TESTING=1 \
ANTLR_JAR_LOCATION=/tmp/antlr-4.8-complete.jar \
GRAMMAR_FILE=grammars/rost.json \
GRAMMAR_FILENAME=rost \
CFLAGS=-trigraphs \
lib/antlr4_shim/generated
Lots of input rules can then be generated, with Bash providing an optional initial random seed:
mkdir -p "$FUZ_OUT/default/" # Args: <max_num> <max_size> <seed_output_dir> <tree_output_dir> [<random seed>] ./Grammar-Mutator/src/grammar_generator-rost 4096 1024 "$FUZ_IN" "$FUZ_OUT/default/" $RANDOM$RANDOM
A new fuzzing process can now get launched:
export AFL_CUSTOM_MUTATOR_LIBRARY=$PWD/Grammar-Mutator/src/libgrammarmutator-rost.so export AFL_CUSTOM_MUTATOR_ONLY=1 afl-fuzz -i "$FUZ_IN" -o "$FUZ_OUT" -- /dev/shm/fuzzing-sys/bin/fast-rost /bin/ls

With mixed inputs
The fuzzing process may produce the best results by mixing dictionary attacks and grammar mutations:
unset AFL_CUSTOM_MUTATOR_ONLY rm -rf "$AFL_TMPDIR" "$FUZ_IN" "$FUZ_OUT" mkdir -p "$AFL_TMPDIR" "$FUZ_IN" "$FUZ_OUT" mkdir -p "$FUZ_OUT/default/" ./Grammar-Mutator/src/grammar_generator-rost 4096 1024 "$FUZ_IN" "$FUZ_OUT/default/" $RANDOM$RANDOM afl-fuzz -i "$FUZ_IN" -o "$FUZ_OUT" -x /dev/shm/rost.dict -- /dev/shm/fuzzing-sys/bin/fast-rost /bin/ls
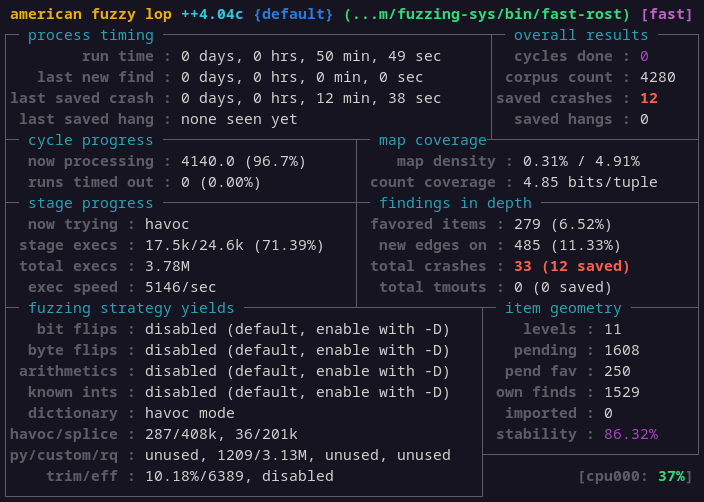
Minimal cases storage
In order to save for further analysis [huge numbers of] inputs leading to buggy states, a small Shell script runs afl-tmin to minimize the test cases leading to crashes and stores the results into the tools/fuzzing/rost/min/ directory:
./tools/fuzzing/rost/minall.sh
The filename for the final rules has the following format: <AFL id>-<SHA256 hash from rule content>.rost.
The script can thus be run as much as needed; it will not overwrite previous rules with new content.
Another script helps to keep the storage directory as clean as possible by removing currently working rules:
./tools/fuzzing/rost/rerun.sh
